Molecular signatures of inherited and acquired sporadic late onset
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 dezembro 2024
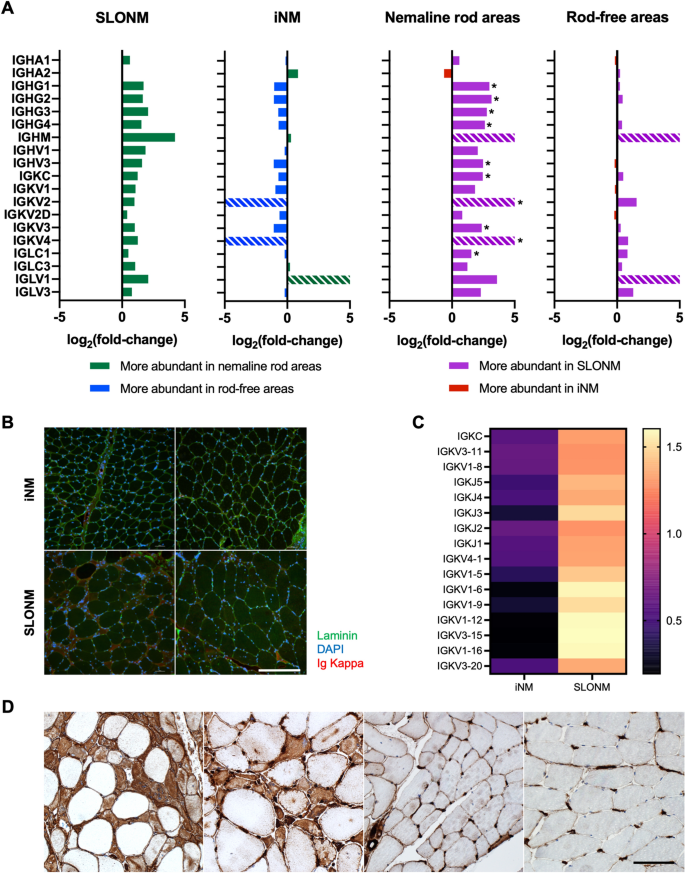
Acquired sporadic late onset nemaline myopathy (SLONM) and inherited nemaline myopathy (iNM) both feature accumulation of nemaline rods in muscle fibers. Unlike iNM, SLONM is amenable to therapy. The distinction between these disorders is therefore crucial when the diagnosis remains ambiguous after initial investigations. We sought to identify biomarkers facilitating this distinction and to investigate the pathophysiology of nemaline rod formation in these different disorders. Twenty-two muscle samples from patients affected by SLONM or iNM underwent quantitative histological analysis, laser capture microdissection for proteomic analysis of nemaline rod areas and rod-free areas, and transcriptomic analysis. In all iNM samples, nemaline rods were found in subsarcolemmal or central aggregates, whereas they were diffusely distributed within muscle fibers in most SLONM samples. In SLONM, muscle fibers harboring nemaline rods were smaller than those without rods. Necrotic fibers, increased endomysial connective tissue, and atrophic fibers filled with nemaline rods were more common in SLONM. Proteomic analysis detected differentially expressed proteins between nemaline rod areas and rod-free areas, as well as between SLONM and iNM. These differentially expressed proteins implicated immune, structural, metabolic, and cellular processes in disease pathophysiology. Notably, immunoglobulin overexpression with accumulation in nemaline rod areas was detected in SLONM. Transcriptomic analysis corroborated proteomic findings and further revealed substantial gene expression differences between SLONM and iNM. Overall, we identified unique pathological and molecular signatures associated with SLONM and iNM, suggesting distinct underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. These findings represent a step towards enhanced diagnostic tools and towards development of treatments for SLONM.

Sporadic Ataxia - National Ataxia Foundation

Genetic and molecular changes in ovarian cancer

Figure 8 from Regional distribution of synaptic markers and APP

Disruption of Fgf13 Causes Synaptic Excitatory–Inhibitory

A microRNA signature that correlates with cognition and is a
Complex II - Bioblast

Ret deficiency decreases neural crest progenitor proliferation and

Principles of Cancer Genetics, 2008, p.333.pdf - Institute of Biology
Human SOX17 Antibody AF1924: R&D Systems

Transcriptomic analysis of inherited and sporadic late-onset
Recomendado para você
-
 Altered Fc galactosylation in IgG4 is a potential serum marker for22 dezembro 2024
Altered Fc galactosylation in IgG4 is a potential serum marker for22 dezembro 2024 -
 Faisal ALASMARI, King Fahad Medical City, Riyadh22 dezembro 2024
Faisal ALASMARI, King Fahad Medical City, Riyadh22 dezembro 2024 -
 The systemic anti-microbiota IgG repertoire can identify gut22 dezembro 2024
The systemic anti-microbiota IgG repertoire can identify gut22 dezembro 2024 -
 Gut microbiota‐derived synbiotic formula (SIM01) as a novel22 dezembro 2024
Gut microbiota‐derived synbiotic formula (SIM01) as a novel22 dezembro 2024 -
 Reinvestigating the Coughing Rat Model of Pertussis To Understand22 dezembro 2024
Reinvestigating the Coughing Rat Model of Pertussis To Understand22 dezembro 2024 -
 Delayed booster dosing improves human antigen-specific Ig and B22 dezembro 2024
Delayed booster dosing improves human antigen-specific Ig and B22 dezembro 2024 -
 Nabwana I.G.G. - IMDb22 dezembro 2024
Nabwana I.G.G. - IMDb22 dezembro 2024 -
 Bishop's Cove Post Production22 dezembro 2024
Bishop's Cove Post Production22 dezembro 2024 -
 Ziggy Marley - Official Merchandise - Sound System T22 dezembro 2024
Ziggy Marley - Official Merchandise - Sound System T22 dezembro 2024 -
 From structure to function – Ligand recognition by myeloid C-type22 dezembro 2024
From structure to function – Ligand recognition by myeloid C-type22 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
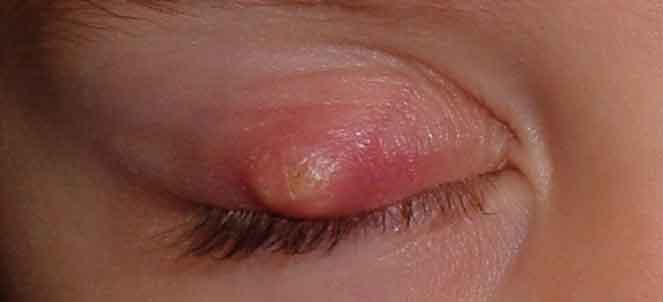 Hordéolo ou Terçolho no olho - o que é, causas, tratamento, cura22 dezembro 2024
Hordéolo ou Terçolho no olho - o que é, causas, tratamento, cura22 dezembro 2024 -
 GIF LORDS — I Forgot to Remember to Forget22 dezembro 2024
GIF LORDS — I Forgot to Remember to Forget22 dezembro 2024 -
 Karla Sayuri cartunista de animes e desenhos em geral – No blog da22 dezembro 2024
Karla Sayuri cartunista de animes e desenhos em geral – No blog da22 dezembro 2024 -
como assistir blue lock dublado na tv|Pesquisa do TikTok22 dezembro 2024
-
 DISHONORED 2 - XBOX ONE22 dezembro 2024
DISHONORED 2 - XBOX ONE22 dezembro 2024 -
 Classic Film Review: The toughest “To Have and Have Not” — “The Breaking Point” (1950)22 dezembro 2024
Classic Film Review: The toughest “To Have and Have Not” — “The Breaking Point” (1950)22 dezembro 2024 -
 Sons of The Forest: Saiba se seu PC poderá rodar o jogo22 dezembro 2024
Sons of The Forest: Saiba se seu PC poderá rodar o jogo22 dezembro 2024 -
Redraw of the Gucci and One Piece collab! 🤩 #animeart #art #anime22 dezembro 2024
-
 Home Argos Scan22 dezembro 2024
Home Argos Scan22 dezembro 2024 -
 5 cursos gratuitos para quem faz licenciatura EaD22 dezembro 2024
5 cursos gratuitos para quem faz licenciatura EaD22 dezembro 2024

