Analysis suggests child bullies have higher risk for substance use later in life
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 dezembro 2024

Children and adolescents who bully their peers have a higher risk for drug, alcohol and tobacco use later in life, according to the results of a meta-analysis published in Pediatrics. Charlotte Vrijen, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands, and colleagues reviewed existing evidence regarding the association between peer bullying perpetration in

Bullying
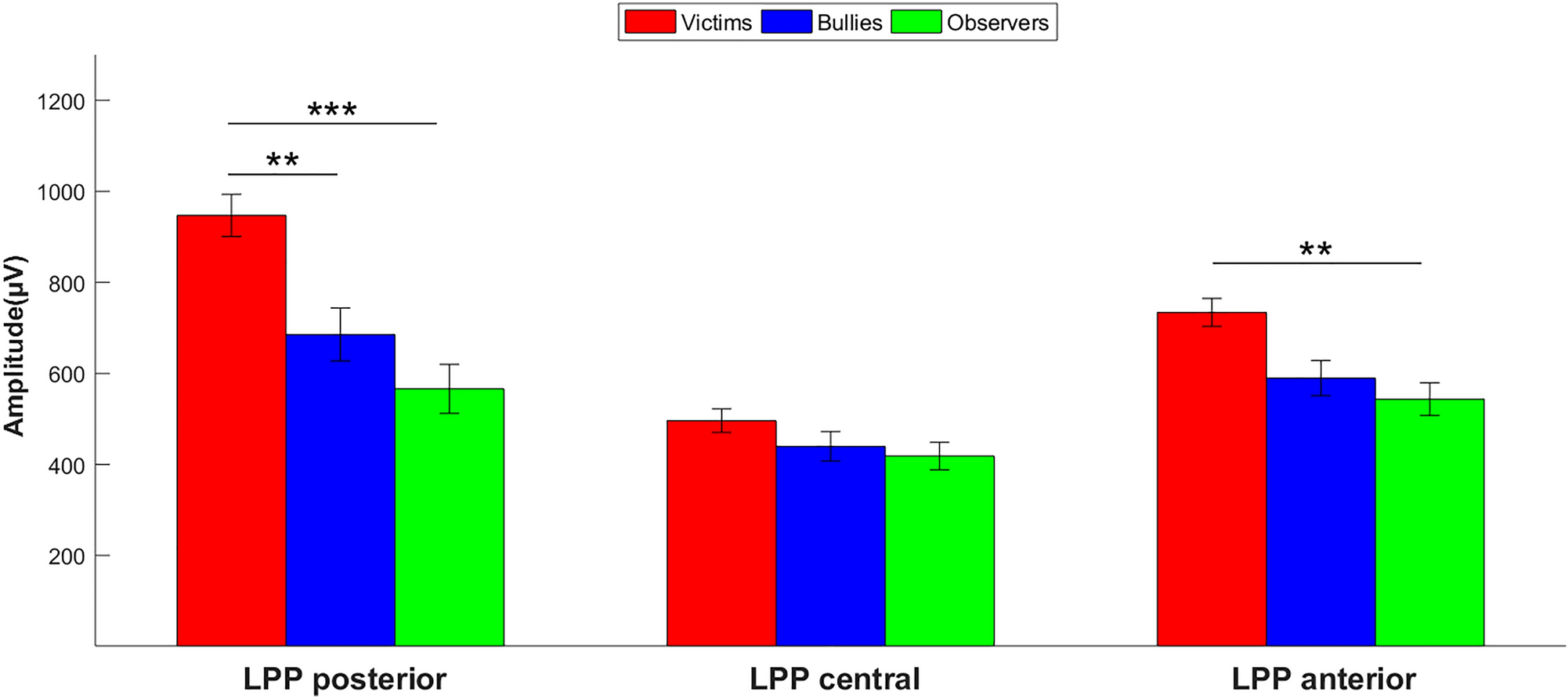
Emotional processing in bullying: an event-related potential study

Childhood Risk and Protective Factors as Predictors of Adolescent Bullying Roles

Global variation in the prevalence of bullying victimisation amongst adolescents: Role of peer and parental supports - eClinicalMedicine

Examining the Effectiveness of School-Bullying Intervention Programs Globally: a Meta-analysis

Impact of Bullying in Childhood on Adult Health, Wealth, Crime, and Social Outcomes - Dieter Wolke, William E. Copeland, Adrian Angold, E. Jane Costello, 2013

Full article: Persistent bullying and the influence of turning points: learnings from an instrumental case study

Childhood and Adolescent Bullying Perpetration and Later Substance Use: A Meta-analysis, Pediatrics
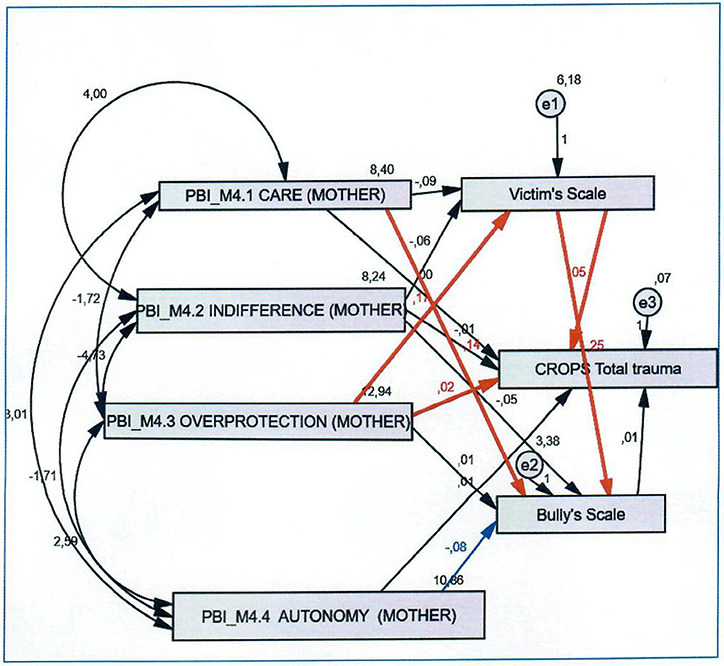
Frontiers School Bullying and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms: The Role of Parental Bonding

School violence and bullying of children with disabilities in the Eastern and Southern African Region: a needs assessment
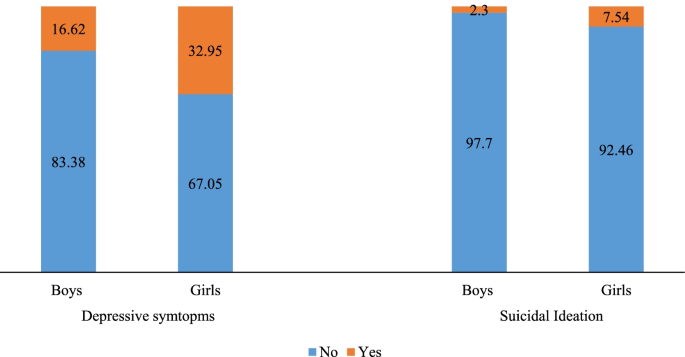
The effects of cyberbullying victimization on depression and suicidal ideation among adolescents and young adults: a three year cohort study from India, BMC Psychiatry

Long-term effects of bullying Archives of Disease in Childhood

Substance use during the pandemic

The Connection Between Low Self-Esteem & Bullying - Video & Lesson Transcript
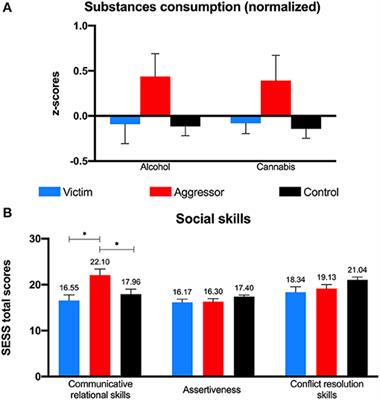
Frontiers Long-Term Profiles of Bullying Victims and Aggressors: A Retrospective Study
Recomendado para você
-
 Here's what you need to know about bullying.31 dezembro 2024
Here's what you need to know about bullying.31 dezembro 2024 -
 The role of social emotional learning in bullying prevention31 dezembro 2024
The role of social emotional learning in bullying prevention31 dezembro 2024 -
 Cyberbullying: How is it different from face-to-face bullying?31 dezembro 2024
Cyberbullying: How is it different from face-to-face bullying?31 dezembro 2024 -
 The most common types of school bullying31 dezembro 2024
The most common types of school bullying31 dezembro 2024 -
 Preventing Bullying - Montgomery County Public Schools, Rockville, MD, Montgomery County Public Schools31 dezembro 2024
Preventing Bullying - Montgomery County Public Schools, Rockville, MD, Montgomery County Public Schools31 dezembro 2024 -
Say NO to bullying > Fairchild Air Force Base > Article Display31 dezembro 2024
-
 Bullying: Online and in the Classroom31 dezembro 2024
Bullying: Online and in the Classroom31 dezembro 2024 -
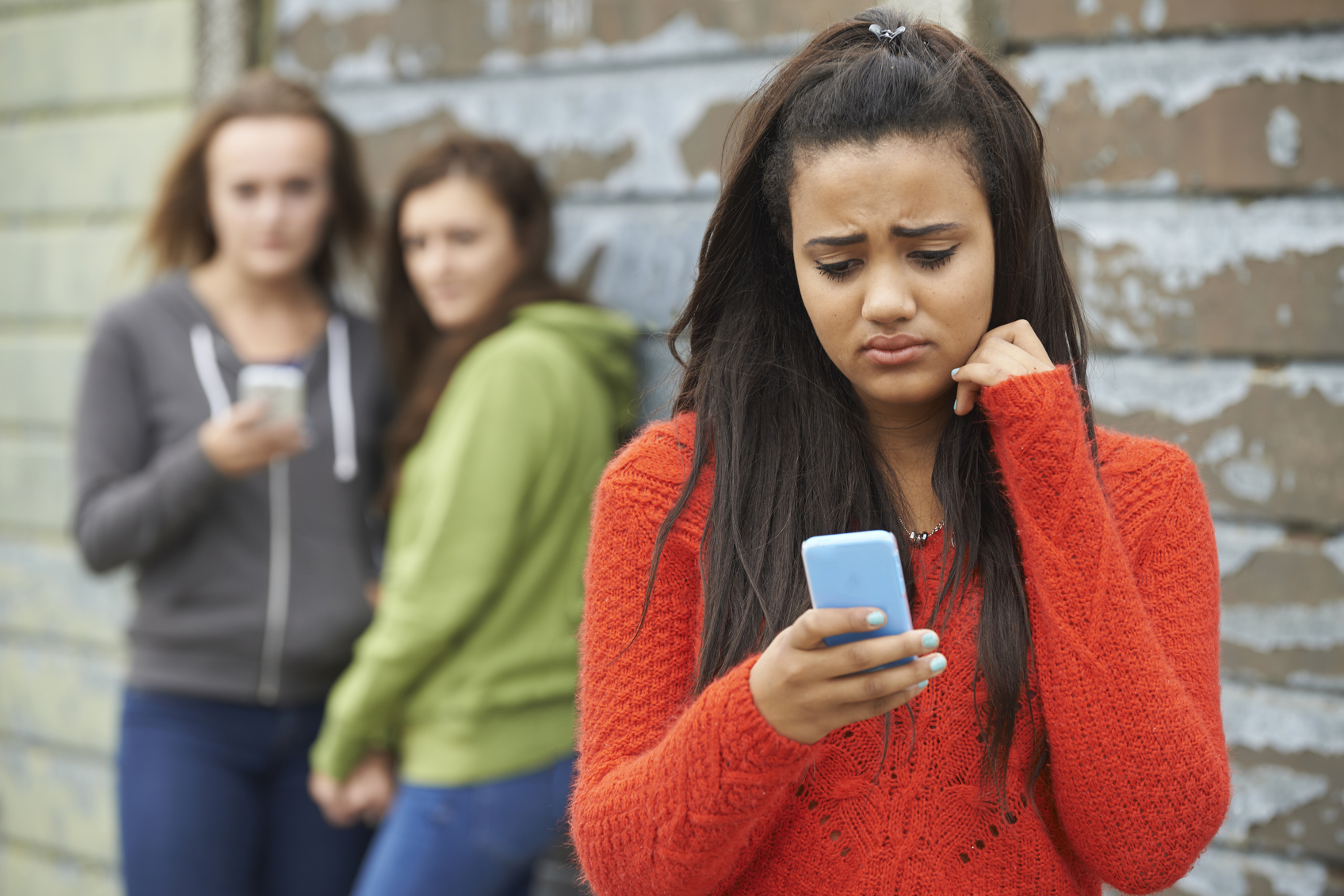 Can Bullying Lead To An Eating Disorder?31 dezembro 2024
Can Bullying Lead To An Eating Disorder?31 dezembro 2024 -
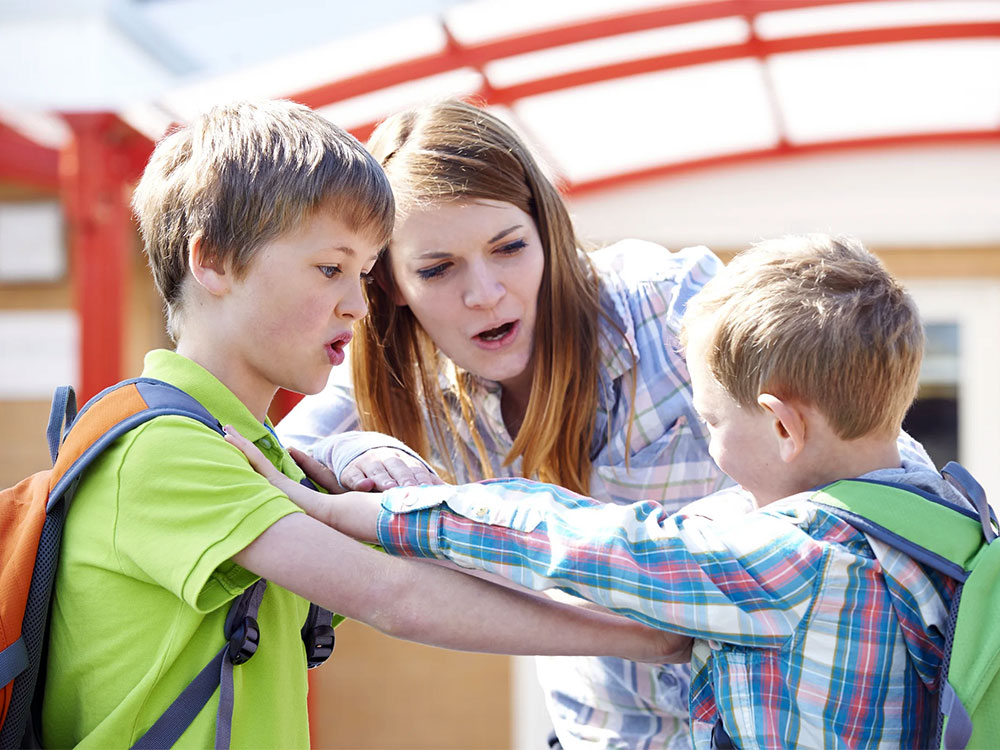 Children bullying others: what to do31 dezembro 2024
Children bullying others: what to do31 dezembro 2024 -
 Teaching about Bullying in the Classroom - Heart and Mind Teaching31 dezembro 2024
Teaching about Bullying in the Classroom - Heart and Mind Teaching31 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
append() and extend() in Python: - Python Coding - Quora31 dezembro 2024
-
 andrei on X: o cara n tem dois caminhos, ou ele vai pra china só pra ficar mais rico (que é válido pra caralho) ou ele fica onde tá e continua jogando31 dezembro 2024
andrei on X: o cara n tem dois caminhos, ou ele vai pra china só pra ficar mais rico (que é válido pra caralho) ou ele fica onde tá e continua jogando31 dezembro 2024 -
is meguru bachira schizophrenic|TikTok Search31 dezembro 2024
-
 Made in Abyss - Season 1 Box Set (Vol. 1-5) On Sale 11/14/202331 dezembro 2024
Made in Abyss - Season 1 Box Set (Vol. 1-5) On Sale 11/14/202331 dezembro 2024 -
 Prime Gaming Free Games for November 2023 Revealed31 dezembro 2024
Prime Gaming Free Games for November 2023 Revealed31 dezembro 2024 -
 Stream Taming io: A Survival .io Game with Magical Pets - Download31 dezembro 2024
Stream Taming io: A Survival .io Game with Magical Pets - Download31 dezembro 2024 -
 mapa 3 sea blox fruits31 dezembro 2024
mapa 3 sea blox fruits31 dezembro 2024 -
 Mako Mermaids Song - Theme song - Wattpad31 dezembro 2024
Mako Mermaids Song - Theme song - Wattpad31 dezembro 2024 -
Quais livros você indica para quem já sabe xadrez, mas não joga muito bem ? - Quora31 dezembro 2024
-
 Roronoa Zoro Archives31 dezembro 2024
Roronoa Zoro Archives31 dezembro 2024

